ISO 42001 Starter Guide
By Burçin Kızılcıklı, Ege Uğur Amasya, Hayriye Anıl, İdil Kula, Nesibe Kırış Can and Onur Pişirir
October 2025
This guide offers a practical, step-by-step interpretation of ISO 42001 to help organizations effectively implement AI governance and manage associated risks. Using visuals and a fictional case study of “X Corporation,” it translates complex standards into actionable strategies that enhance compliance, transparency, and trust.
AuthorS

Research Fellow

Research Fellow

Research Fellow

Research Fellow

Research Fellow

Research Fellow
Advisor & Mentor
Advisor & Editor
Originally Published
October 2025
Executive Summary
As AI becomes advanced day by day, organizations are automating critical functions at a growing pace. While efficiency and innovation drive the adoption of AI, significant risks, such as regulatory noncompliance, ethical breaches, and loss of stakeholder trust, must also be addressed. Risk management is essential for organizations to remain competitive in this environment.
Global standards for AI governance are emerging; however, the definition of a trustworthy AI system still remains unsettled. Aligning with established frameworks, such as the EU AI Act, the NIST AI Risk Management Framework, and ISO 42001, provides organizations a strategic advantage. These standards support reliability, accountability, transparency, and thorough documentation. Following them reduces compliance risks and strengthens stakeholder confidence.
Although interest in ISO 42001 is increasing, most guides lack actionable insights. They often emphasize abstract clauses and definitions, with few practical tools or real-world examples. This leaves many organizations struggling to apply the standard effectively.
This guide addresses that gap by providing a clear, practical interpretation of ISO 42001 for organizations at any stage of AI adoption. It defines key implementation roles, explains each clause of the standard, and demonstrates real-life applications. The fictional case study of “X Corporation” illustrates the implementation of an AI-based HR tool from concept through deployment and oversight.
The guide utilizes visual aids, including detailed and comprehensive tables and diagrams, to enhance clarity and usability. It also maps ISO 42001 clauses with practical insights from the fictional story of “X Corporation”, providing step-by-step guidance. The result is a concise, actionable, and sector-agnostic resource for organizations applying AI governance principles when deploying AI.
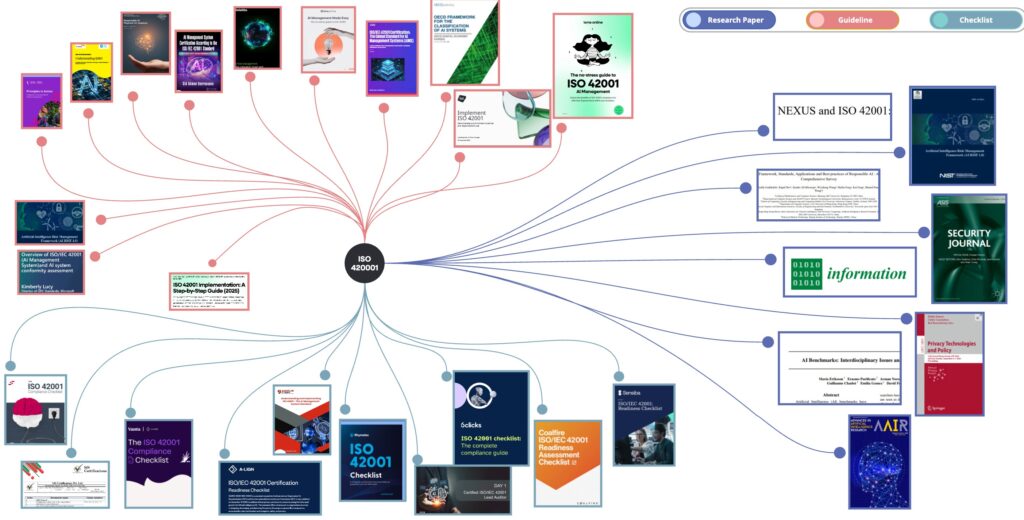
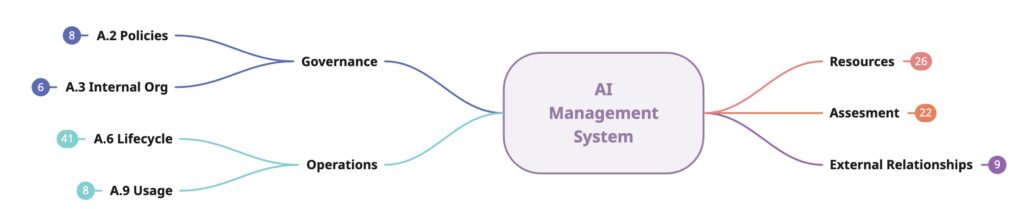
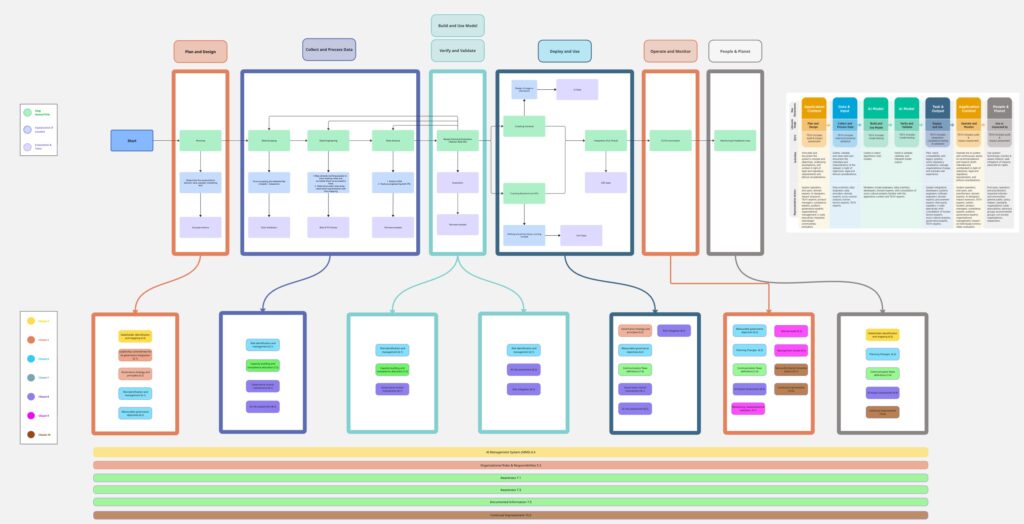
Conclusion
The ISO 42001 standard provides a widely accepted, auditable framework for AI adoption goals of organizations, and our guide:
- Introduces ISO 42001 and AI Management System (AIMS).
- Translates the concepts, clauses, and requirements of the ISO 42001 document into plain language, illustrating them through a detailed use case and diagrams.
- Lists relevant standards and frameworks and explains their relations.
- Defines the key roles necessary for implementing the standard.
- Introduces each clause on a theoretical basis.
- Grounds each clause in real-world applications by providing examples and types of tools that can be used, illustrated through a fictional case study of X Corporation’s complete lifecycle steps in implementing an AI HR tool.
- Incorporates abundant tables and diagrams to ensure engagement and understandability.
- The document is easy to read and follow.
- The fictional story example of X Corporation draws an example for organizations and gives perspective on how applications of the principles of ISO 42001 can be applied in a real organizational context.
In today’s ever-innovating world, adopting a reliable AIMS is essential for long-term success, enabling organizations to manage risks, build trust, and align AI with societal expectations. Still, as seen in the fictional case of X Corporation, negative connotations may arise, such as fines due to regulatory noncompliance, loss of stakeholder trust resulting from a security breach, or a violation of ethical and societal expectations. The ability to tackle these risks determines who thrives and who trails in the modern-day market.
Achieving reliability, accountability, and transparency is possible with the right mix of standards and frameworks. Getting compliant with ISO 420001 supports organizations to help withstand regulatory scrutiny and earn the trust of stakeholders and consumers. This is also important for achieving a healthier and safer AI ecosystem and economy for the good of society. However, not all organizations have resources for compliance. At times, businesses lack access to sufficient resources for compliance under poor financial conditions, due to factors such as geopolitics, disability, and gender. To get to that fair point, there is a need for orientation towards trustworthy AI adoption.
Acknowledging the access gap, this guide aims to lead organizations in AI adoption and development. Our approach merges abstract clauses with practical insights through examples. It is designed to be easily understood by any interested reader. Thus, organizations can have a better comprehension of ISO 42001 and be more adaptable in turning standards into action.




